The report Future of Money, co-authored by Subhendu Panigrahi and Ashish Fafadia, sheds light on the evolving landscape of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and their role in the monetary ecosystem. In this two-part thesis, we embark on a comprehensive exploration of these topics, presenting a compelling case supported by data and analysis.
We envision the future of money and payments, with Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) emerging as a pivotal element that is poised to replace physical cash in the coming decade. Backed by central banks and driven by blockchain technology, CBDCs promise enhanced efficiency, security, and financial inclusion, transforming domestic payment systems worldwide.
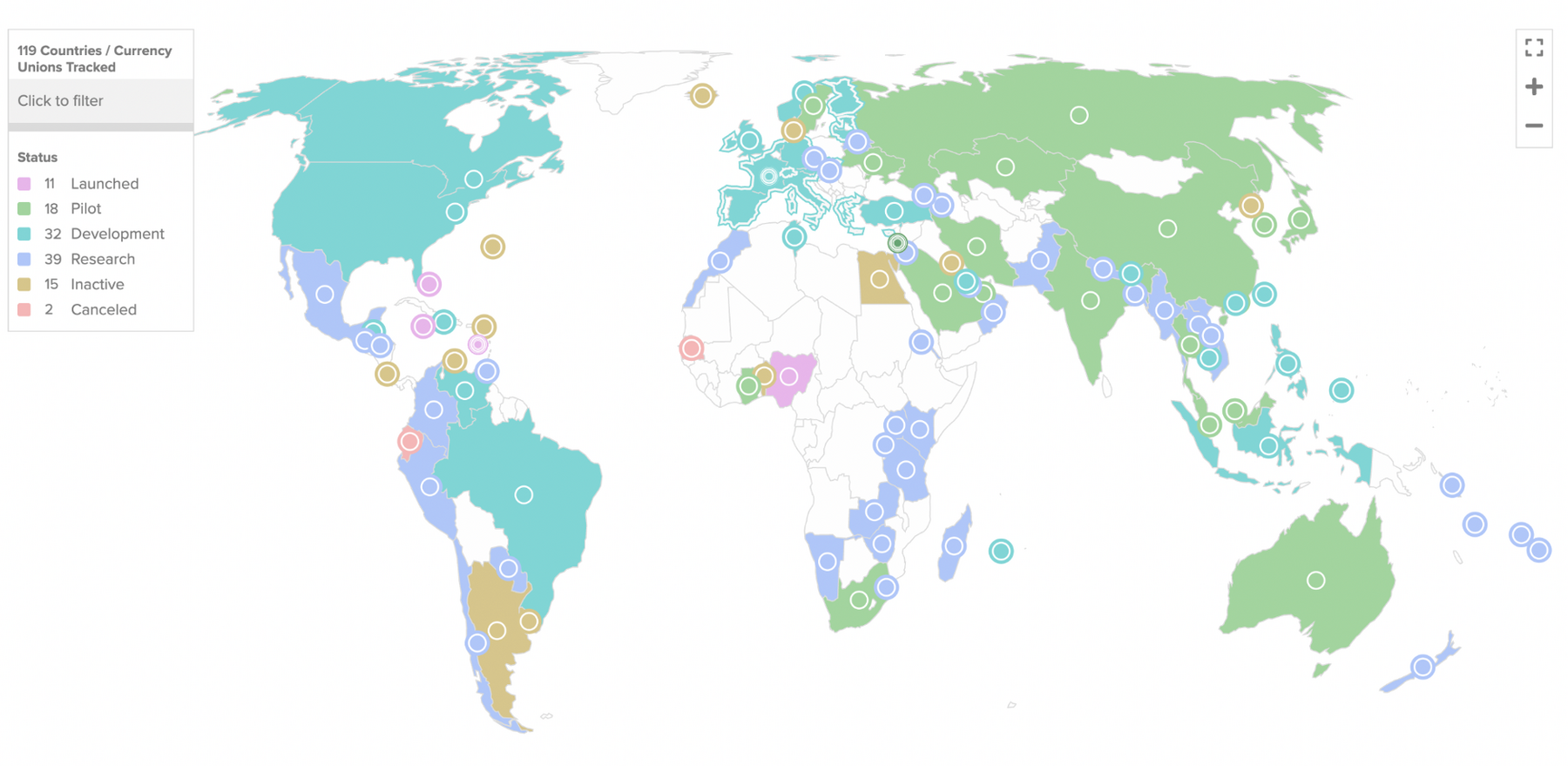
114 countries, representing over 95 percent of global GDP, are exploring a CBDC. In May 2020, only 35 countries were considering a CBDC. A new high of 60 countries are in an advanced phase of exploration (development, pilot, or launch). The exhibit below shows a heatmap of countries currently working at CBDC and their stages of development.
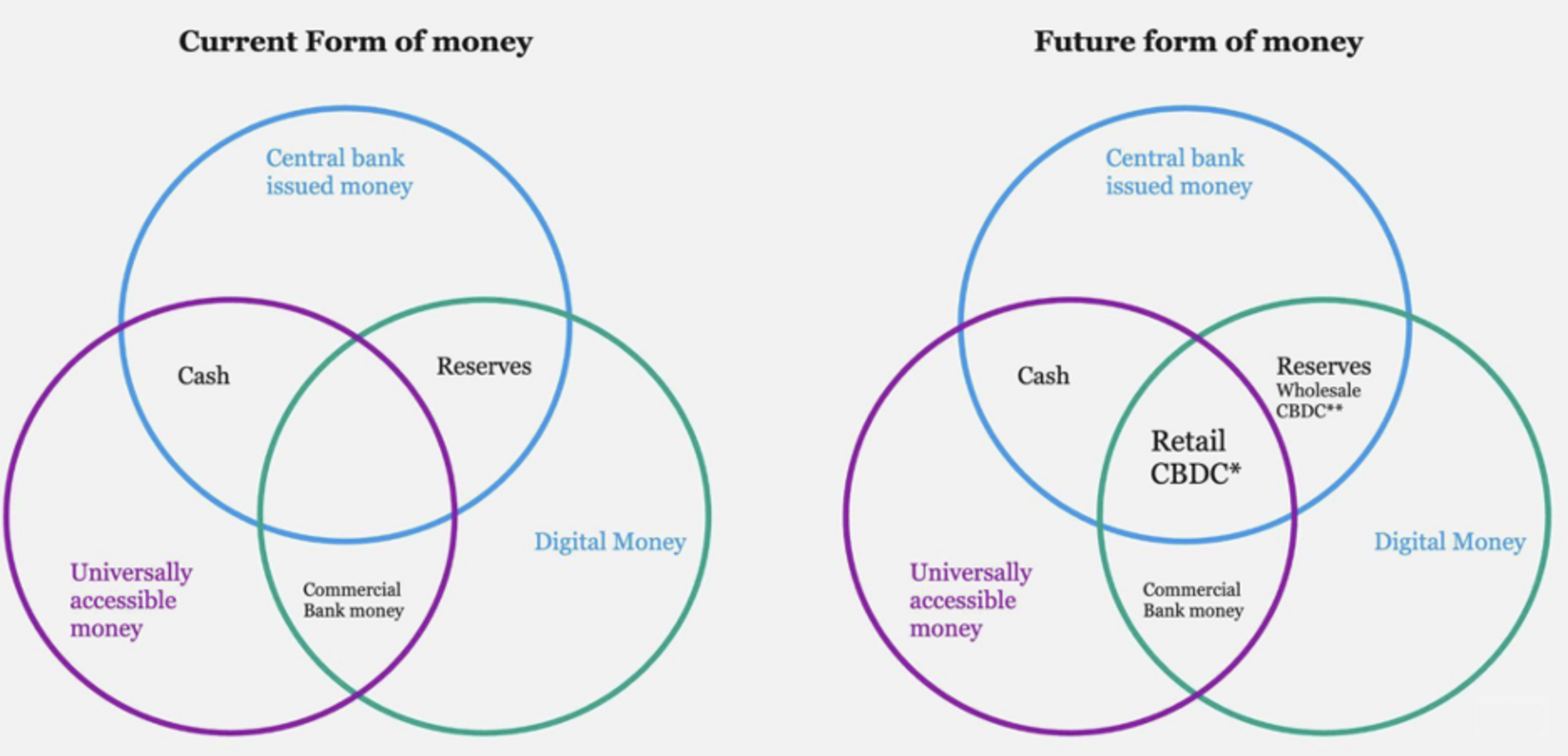
Central banks are working with BIS, IMF, and other industry bodies to come up with CBDC, which is not just a digital-native version of traditional notes and coins but goes beyond the current digital money, which is commercial bank money. Interestingly, the rise of cryptocurrencies and their associated challenges has spurred central banks worldwide to explore and innovate in the realm of digital currencies.
CBDCs offer a government-backed digital alternative to cryptocurrencies, aiming to address some of the drawbacks of traditional cryptocurrencies and create a more regulated and secure digital monetary system. The exhibit below shows how CBDC is represented as the future of money.
Countries like China, Singapore, and India are at the forefront of the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) revolution.
India has also started the pilot in Dec 2022. The users can do both P2P and P2M transactions. However, there is an ongoing debate on why India needs CBDC when it has a robust UPI ecosystem. We have addressed that in our thesis and covered the CBDC and UPI ecosystem in detail
In fact, RBI Governor Shatikanta Das recently clarified the differences between CBDC and UPI stating - “In CBDC, you will draw the digital currency and keep it in your wallet on your mobile. When you make a payment at a shop or to another individual, it will move from your wallet to their wallet. There is no routing or intermediation of the bank.”
Key Technology Driving CBDC
As a key element in this transformative landscape, we delve into the potential of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) and blockchain. Our analysis demonstrates that blockchain technology, serving as the new digital equivalent of paper, holds the promise of revolutionizing various aspects of the monetary ecosystem. We explore how blockchain is establishing commercial banks as pioneers in the evolving financial landscape.
One of the most significant advantages of using blockchain technology in finance is the increased transparency it provides. The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for transactions to be recorded on a shared ledger that is viewable by all parties involved. This level of transparency can significantly reduce the risk of fraud and errors, leading to a more secure and efficient financial system.
As we explore the dynamic interplay between blockchain and the future of money, our thesis seeks to offer valuable insights into the trajectory of financial services and payment methods. We anticipate that our findings will inspire governments, businesses, and individuals to embrace blockchain technology as the catalyst for a more advanced and equitable monetary landscape. With meticulous research and thoughtful analysis, we aim to contribute to the ongoing dialogue on the future of money and its inevitable association with blockchain technology.
Benefits of CBDC
CBDCs have the potential to enhance financial inclusion by providing a safe and affordable means of payment and transfer for people who do not have access to traditional banking services. This is particularly relevant in developing countries, where a significant portion of the population remains unbanked. By leveraging the programmability and security features of CBDCs, startups can develop innovative financial solutions that cater to this underserved market.
CBDCs and deposit tokens are poised to be game-changers in the financial world. With their programmability, security, and efficiency, these digital currencies offer a plethora of opportunities for innovation in the fintech industry.
Moreover, our thesis also highlights the crucial role of commercial banks in driving cross-border payments by leveraging deposit tokens, a cutting-edge solution introduced by major players like JPMorgan Chase (JPMC). These digital representations of fiat currency, powered by blockchain, enable faster and more efficient cross-border transactions, the transformative potential of blockchain and DLT in the future of money. By envisioning a financial ecosystem driven by CBDCs and deposit tokens, we underscore the significance of these technologies in fostering a more inclusive and efficient monetary system globally.
Deposit tokens, in particular, could capture the cross-border and B2B payments market faster than CBDCs due to interoperability issues between different CBDCs. Nonetheless, CBDCs can still be leveraged by startups to create a range of financial products and services, such as purpose-bound money platforms, decentralized exchanges, and cross-border remittances.
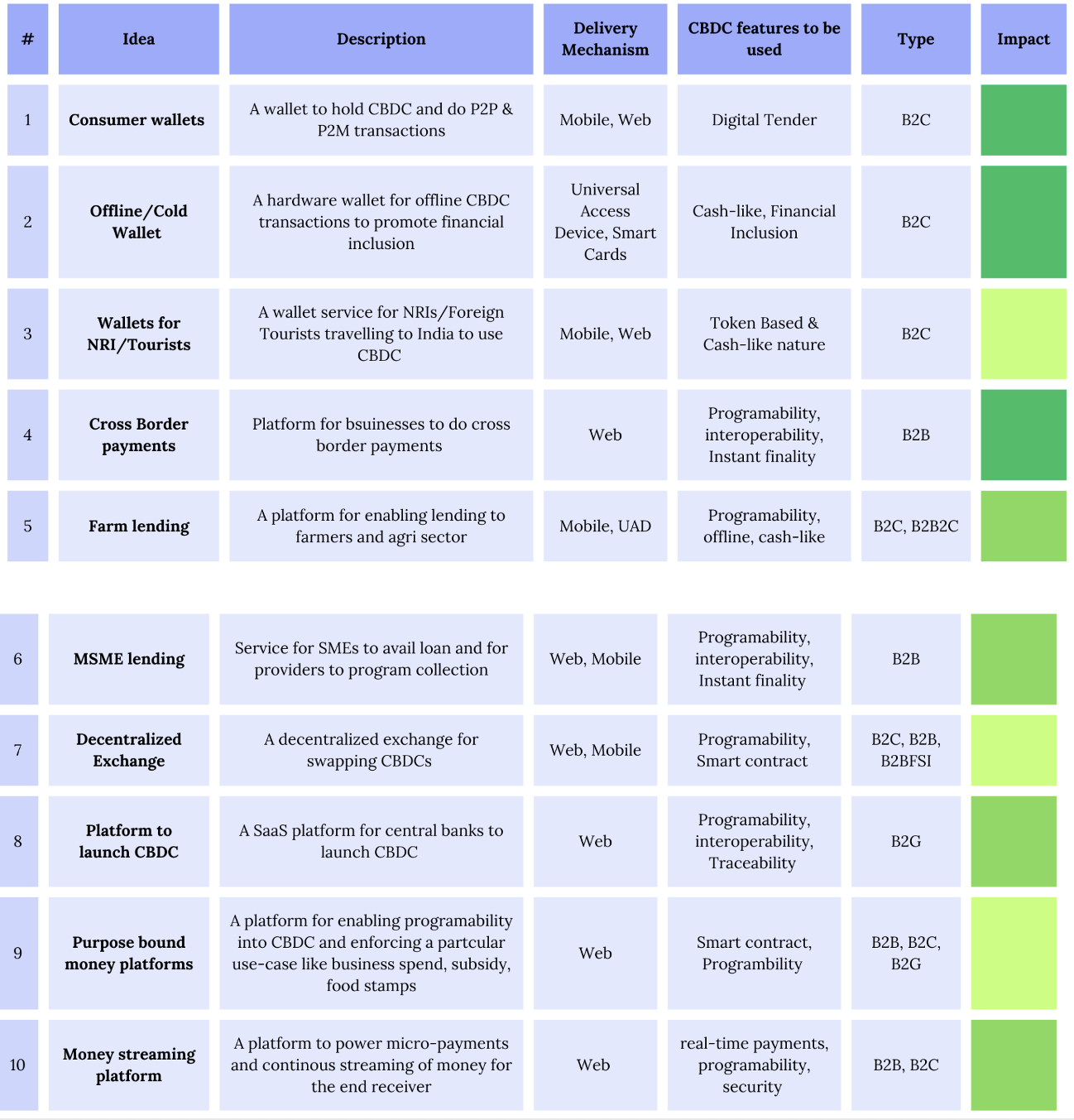
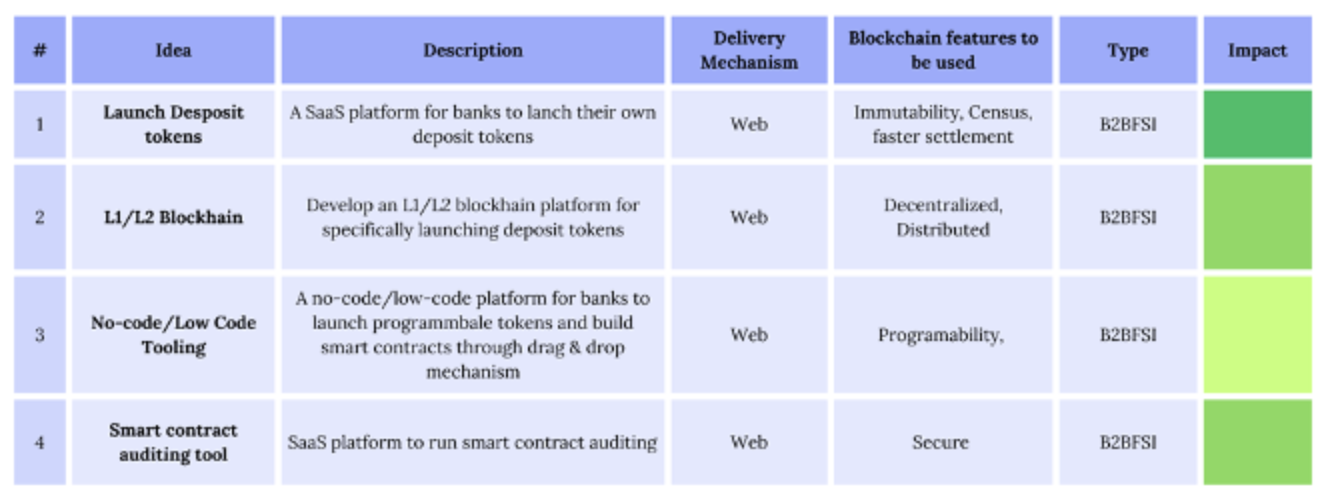
Ideas based on CBDC and Deposit Tokens ecosystem
We have proposed a strong foundation of 10 ideas for the upcoming CBDC ecosystem and 4 ideas for the CMBT (Deposit Tokens) ecosystem for founders and builders depicted below. These ideas cover various categories, such as consumers, businesses, financial institutions, and government, taking into account the current fiscal and regulatory policies. These concepts will evolve as CBDCs gain acceptance among consumers and businesses in the future.
Our research also delves into the role of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which is considered a store of value rather than the future of money itself. Additionally, we examine the efficacy of stablecoins in facilitating peer-to-peer (P2P) and smaller transactions, identifying their relevance within the financial ecosystem.